CCS Technology Can Reduce CO2 Gas Emission Problems Related to Natural Gas Production
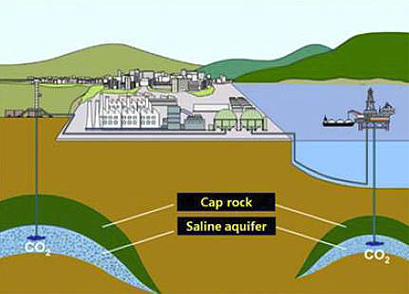
Indonesia plans to reduce emissions CO2 by 26% in 2020 However, large amounts CO2 released into the atmosphere during production natural gas in gas fields viewed as problems for achievement this goal. This problem can be resolved by creating a system for carbon dioxide capture and storage (CCS ) technology – where CO2 emitted during production natural gas captured and sealed into the ground – as a means directly reducing emissions CO2. This project will conduct research and storage development CO2 underground and technology monitoring in the field gas Gundih in Central Java, where it is produced natural gas scheduled to start.
The goal of the project is to develop technology geology and geophysics subsurface for evaluate storage CO2 inside in and around gas fields and for monitoring injection movement CO2 for ensuring distribution and behavior CO2 in storage. The results achieved will be used to systematize technology CCS for underground storage safe from CO2 emitted during production natural gas and help reduce emissions CO2 on a global scale.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is the process of capturing CO2 waste from a source such as a fossil fuel power plant (including from natural gas production activities) and storing it in an underground geological formation so that it does not enter the atmosphere. The goal is to prevent the release of large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere. Although Co2 has been injected into geological formations for decades for various purposes, including enhanced oil recovery, long-term storage of CO2 is a relatively new concept. The first commercial example was Weyburn in 2003 which could be used to describe the removal of CO2 from the air as a geoengineering technique.